

current position:Information and data>brush plating
Brush plating is also known as metal pen plating or rapid plating. With the help of electrochemical methods, the process of forming a metal coating layer by discharging and crystallizing metal ions on the surface of the negative electrode (workpiece) is performed by using a plating pen soaked in the plating solution as the anode. The plating pen is an insoluble anode, and the plating solution adopts a metal salt aqueous solution of organic complexes. During brush plating, the plating pen is in contact with the surface of the workpiece and moves continuously.
Overview
Basic Principles of Brush Plating
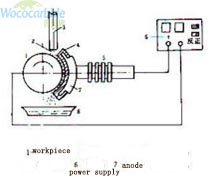
Brush plating is an electroplating method that relies on a pad or brush in contact with the anode to provide the electrolyte required for electroplating. During electroplating, the pad or brush moves on the cathode to be plated. Brush plating uses a specially developed series of brush plating solutions, various forms of pens and anodes, and dedicated DC power supplies. When working, the workpiece is connected to the negative pole of the power supply, the plating pen is connected to the positive pole of the power supply, and the surface of the workpiece is wiped by the wrapped anode immersed in the solution. And it gradually thickens with time. Because the workpiece and the coating pen have a certain relative speed, it is an intermittent crystallization process for each point on the coating.
Technical characteristics of brush plating
The formation of the brush plating layer is essentially the same as that of the tank plating, which is a process in which the metal ions in the solution are discharged and crystallized on the negative electrode (workpiece). However, compared with tank plating, the brush plating pen and the workpiece have relative motion, so the plated surface does not undergo metal ion reduction crystallization at the same time, but instantaneous discharge crystallization occurs at each point of the plated surface when the plating pen is in contact with it. Therefore, brush plating technology has its own unique features in terms of technology, and its characteristics can be summarized as follows:
1. The equipment is simple, does not require a plating tank, is easy to carry, and is suitable for field and on-site repairs. Especially for the on-site repair of large and precise equipment without disassembly, it has more practical value.
2. The process is simple and the operation is flexible. Do not use a lot of materials to protect the parts that do not need to be plated.
3. During the operation, the cathode and the anode have relative motion, so it is allowed to use a higher current density, which is several times to dozens of times larger than the current density used in tank plating.
4. The metal ion content in the plating solution is high, so the plating speed is fast (5 to 10 times faster than tank plating).
5. There are many types of solutions and a wide range of applications. There are more than 100 solutions for different purposes, which are suitable for different needs of various industries.
6. The performance of the solution is stable, and it does not need to be tested and adjusted during use; it is non-toxic and has little environmental pollution; it is non-flammable and non-explosive, and it is easy to store and transport.
7. Equipped with special electrolytic solution for degreasing and rust removal, so the surface pretreatment effect is good, the coating quality is high, and the bonding strength is large.
8. There are different types of plating pens, and are equipped with insoluble anodes of different shapes and sizes, which can be repaired for various parts with different geometric shapes and complex structures. Some anodes can also use soluble anodes.
9. Low cost and great economic benefits.
10. Mechanical processing is generally not required after plating.
11. A set of equipment can be brushed on a variety of materials, and dozens of coatings can be plated. It is very convenient to obtain a composite coating, and a layered structure can be used to obtain a large thickness coating.
12. The uniformity of the coating thickness can be controlled, either uniformly or unevenly.
Disadvantages of brush plating technology:
1. In the process of reciprocating dipping in the plating solution, the proportion of auxiliary time is large, the deposition speed is slow, and the operation labor intensity is high;
2. When the anode is close to the workpiece, part of the plating solution will be extruded directly into the waste solution without being deposited, so the utilization rate of the plating solution is low. In addition, the gauze, cotton, etc. used to wrap the anode can not be recycled generally, and the economy is poor;
3. The work efficiency of manual brush plating is low, and the process parameters are affected by the operator's factors, which is difficult to control at a stable level, and it is difficult to achieve mass production
4. The brush-plated coating of the electric brush-plating process is subject to the greatest amount of wear. Generally, the brush-plating thickness of the brush-plated coating is less than 0.2mm. When the wear amount is greater than 0.2mm, the brush plating efficiency will be doubled, and when the brush plating layer is too thick, the brush plating layer is easy to fall off during use, and the service life is short.
Application of brush plating technology
1. Repair the defects of tank plating products.
2. Repair the surface wear of out-of-tolerance parts and parts, and restore their dimensional accuracy and geometric shape accuracy. 3. Repair scratches, grooves, pits and pitting on the surface of parts.
4. Strengthen the surface of the new product to make it have higher mechanical properties and better physical and chemical properties.
5. Prepare the protective layer on the surface of the parts. If the surface is required to be resistant to corrosion, high temperature and oxidation, the surface of aluminum and aluminum alloys should be oxidized.
6. Complete the operations that are difficult to complete in tank plating. Such as:
(1) The parts are too large or require special requirements to be bath-plated.
(2) The workpiece is difficult to disassemble or disassemble and the transportation cost is expensive, and the large equipment is repaired on site.
(3) Large pieces or blind holes only need to be partially plated.
(4) Parts immersed in the plating tank will cause damage to other parts or contaminate the plating solution.
Brush Plating Equipment
Modern brush plating technology requires special equipment and tools. It includes a power supply unit, a complete set of pen-plating tools and replaceable anodes and wrapping materials, as well as rotating tires and other auxiliary tools for holding parts.
Brush Plating Power Supply
The power supply is the main equipment for implementing brush plating, and it is a device used to provide electrical energy. Therefore, the following design requirements must be met:
1. The power supply must have the function of changing alternating current to direct current, and it is required that when the load current changes within a large range, the voltage change is small. 2. The output voltage should be steplessly adjustable to meet the needs of various processes and different solutions. The adjustable range of common power supply voltage is 0V ~ 30V, and the maximum voltage of high-power power supply can reach 50V.
3. The self-adjusting function of the power supply is strong, and the output current should be automatically adjusted with the change of the contact area between the plating pen and the anode. 4. The power supply should be equipped with a device for directly or indirectly measuring the thickness of the coating to display or control the thickness of the coating. 5, with overload protection device. When overloaded or short-circuited, the main circuit can be quickly cut off to protect the safety of equipment and personnel. 6. The power supply should be small in size, light in weight, reliable in operation, simple in operation and convenient in maintenance.
There are many domestic manufacturers producing brush-plating power supplies, which generally have three types: constant voltage, constant current, and pulsed by their control and output forms. Its components and working principles are basically the same, generally mainly composed of rectifier, ampere-hour meter, overload protection circuit and some other auxiliary circuits.
Brush Plating Pen
The plated pen is composed of an anode and a plated pen holder, and the plated pen holder includes a conductive rod, a radiator, an insulating handle, and the like.
1. Classification and selection of anodes
According to the materials used, anodes can be divided into: graphite anodes, platinum-iridium alloy anodes, stainless steel anodes, soluble anodes and anodes of other materials. In order to meet the needs of workpieces of different shapes and sizes, the anode can be made into various shapes such as cylinder, semicircle, crescent, flat plate, square bar, line and so on. In practice, the shape and size of the anode to be selected should be determined according to the shape and size of the surface of the workpiece to be plated. For example: wire-shaped anodes are suitable for filling grooves and pits; cylindrical anodes are used for inner diameters or facets, semi-circular anodes are used for inner holes or flat surfaces; crescent-shaped anodes are used for outer circles; flat-shaped anodes are used for flat surfaces or outer circle, etc.
Generally small area brush plating, the designed anode working area accounts for 1/5~1/3 of the plated area is the best. However, when brushing a large area, due to the limitation of the size and strength of the material, it is impossible to make a large anode, so it can only be used according to the size of the existing material.
2. Anode packaging and packaging materials
The outer surface of the anode is not allowed to be directly used for brush plating unless it is wrapped with a suitable material. The function of the anode wrapping is to store the plating solution and prevent the anode and the workpiece from directly contacting and short-circuiting, so as not to burn the workpiece. At the same time, it can mechanically filter the graphite particles and other impurities corroded from the anode surface.
The commonly used wrapping materials are mainly medical absorbent cotton, polyester cotton sleeves, or artificial wool sleeves. When wrapping, generally wrap a layer of absorbent cotton of appropriate thickness on the surface of the anode, and then wrap it with polyester cotton cover or artificial wool cover.
The packaging of the anode is mainly to wrap the surface in contact with the workpiece. The steps and methods for wrapping the cylindrical and flat anodes are: (1) Tear the absorbent cotton into sheets (thickness is about 3mm-6mm). (2) Cut the cotton into strips with scissors according to the shape and size of the anode.
(3) Wrap the outer surface of the anode with a cotton strip. The beginning and end of the cotton should be pulled into a wedge shape, so that the cotton cover is tight and even. (4) Choose an appropriate size polyester cotton sleeve to cover the cotton, and tie it tightly with a rubber band to improve the wear resistance of the cotton sleeve.
The thickness of the coating layer of the anode should be uniform and appropriate. When it is too thick, although there is a lot of plating solution stored, the resistance is large and the deposition speed is slow. When it is too thin, there is less plating solution stored and it is easy to wear through, causing local overheating of the workpiece, or even short circuit, which affects the quality of the coating. The thickness of the cover is generally 5mm to 15mm (referring to the cover in the virtual state).
3. Use and storage of plated pen
In brush plating, there must be one or several dedicated pens for each solution. Before each plating pen is used, the name label of the plating solution used must be affixed to the pen barrel, and cannot be mixed.
After use, the pens should be rinsed with clean water and stored separately. They cannot be mixed, let alone mixed, especially copper-plated and nickel-plated pens should not be mixed to avoid mutual contamination of the plating solutions. Before using the plating pen next time, you should pay attention to check whether there is rust at the cable jack. If there is rust, disassemble and clean it up.
The graphite anode will also be corroded after long-term use. You can use tools such as files and scrapers to scrape off the surface corrosion and continue to use it. Excessive corrosion will be scrapped.
Once the anode casing is worn out, it should be replaced in time. The replaced cotton is generally not reusable. Cleaner cotton can be rinsed with water and used after drying.
When the used plating pen is no longer used for a long time, the anode, locking nut, conductive rod and radiator should be disassembled separately, cleaned and stored separately for reuse.
Brush Plating Auxiliary Appliances and Materials
1. Turn tires
It is a device used to hold parts for rotation. In order to meet the requirements of the relative movement speed between the cathode and the anode and reduce the labor intensity, it is an indispensable equipment for the brush plating of shaft parts.
2. Liquid cup, plastic tray, squeeze bottle
The liquid cup is used to hold the plating liquid, the plastic tray is used to recover the plating liquid or waste water, and the squeeze bottle is used to hold the flushing water or the plating liquid as an appliance for supplying the plating liquid.
3. Portable motors, various small grinding wheels, oil stones, scrapers
These are an indispensable set of tools for cleaning and reshaping workpiece defects such as scratches, grooves, pits, and trimming coatings. 4. Insulation tape, plastic cloth
Insulating tape and plastic sheeting are used to stick and mask the non-plated surface of the workpiece to prevent contamination and corrosion. 5. Scissors, rubber band, needle and thread
Scissors are used to cut cotton and polyester-cotton sleeves, rubber bands are used for bundling wraps, and needles and threads are used to sew the wraps.
Brush Plating Solution
Brush plating solutions have distinct characteristics compared to slotted plating solutions. Most metal plating solutions are aqueous solutions of organic chelates;
Except for a small part of the plating solutions (gold and silver) with special requirements, the rest of the plating solutions do not contain cyanide; the metal ion content in the plating solution is high, and the deposition rate is fast; some solutions are acidic or alkaline, and most solutions Its pH value is between 4 and 10, and its corrosiveness is small. The deposition rate of acidic baths is generally faster than that of alkaline baths, but acid baths are generally not suitable for direct plating on loose-structured materials; alkaline baths and neutral baths have slower deposition rates than acidic baths, but Their coating process performance and mechanical properties of the coating are relatively good.
The brush plating solution is divided into five categories: surface pretreatment solution, single metal plating solution, alloy plating solution, stripping solution and passivation solution, with a total of 18 systems and more than 100 varieties.
The quality of the brush plating solution is directly related to the repair quality of the workpiece. Generally speaking, the solution used for brush plating has the following requirements:
(1) When the solution is not used for a long time, there should be no precipitation, discoloration or deterioration;
(2) The concentration of metal ions in the plating solution is relatively constant;
(3) The utilization rate of the plating solution is high, and the used waste solution has little or no pollution to the environment;
(4) The plating solution has less damage to the human body or is a green and environmentally friendly plating solution.
Brush Plating Surface Pretreatment Solution
The solutions used for surface pretreatment mainly include electrolytic degreasing solution (electro-cleaning solution) and activation solution for surface electrolytic etching (rust removal).
Brush plating No. 1 electric cleaning solution
The solution is a colorless and transparent alkaline aqueous solution with pH=13 and freezing point of -10℃. It can be stored for a long time and is less corrosive. No. 1 electrolytic cleaning fluid has strong degreasing ability and slight rust removal effect, and is suitable for electrolytic degreasing of all metal surfaces. Its operating process specifications are:
Working voltage 8V~15V
Relative movement speed 60mm/s~130mm/s
Positive connection of power supply (except high-strength steel)
Brush plating No. 0 electric cleaning solution
This is a degreasing solution with similar performance to No. 1 Electrocleaner. Colorless and transparent, pH=13, freezing point of -10℃, can be stored for a long time. The degreasing effect of No. 0 electro-cleaning fluid is better than that of No. 1 electro-cleaning fluid, especially suitable for loose materials such as cast iron. The operating process specification is:
Working voltage 8V~15V
The relative movement speed is 60mm~130mm, the polarity of the power supply is positive
Brush Plating No. 1 Activation Solution
The solution is colorless and transparent, acidic, pH=0.4, freezing point is -15℃, and can be stored for a long time. No. 1 activation solution has the ability to remove the oxide film and fatigue layer on the metal surface, and corrodes the substrate slowly. It is suitable for surface activation treatment of low-carbon steel, low-carbon alloy steel and white cast iron. During activation, operate according to the following process specifications:
Working voltage 8V~15V
Relative movement speed 100mm/s~160mm/s The polarity of the power supply is positive or reverse
Brush Plating No. 2 Activation Solution
The pH of the solution is 0.3, it is colorless and transparent, the freezing point is -17℃, and it can be stored for a long time. No. 2 activating solution has strong ability to remove oxide film and fatigue layer on metal surface, and corrodes quickly to substrate. It is suitable for medium carbon steel, medium carbon alloy steel, high carbon steel, high carbon alloy steel, aluminum and aluminum alloy, gray Activation of cast iron, nickel layers and refractory metals. Can also be used to remove metal burrs and ablate coatings. The operating process specification is:
Working voltage 6V~14V
Relative movement speed 100mm/s~160mm/s Power supply polarity reversed
Brush Plating No. 3 Activation Solution
No. 3 activation solution is light green, pH=4, freezing point is -9℃, and can be stored for a long time. No. 3 activation solution has weak effect on ferrite matrix, or even does not work, but has a strong effect on carbide. Therefore, in addition to being used alone when activating a few materials such as copper, it is generally used in conjunction with other activation solutions (No. 1 and No. 2). The main purpose is to remove the carbon black layer on the surface of medium and high carbon steel, cast iron and other materials activated by No. 1 and No. 2 activation solutions, so as to improve the bonding strength of the coating layer and the substrate. Its operating process specifications are:
Working voltage 10V~25V
The relative movement speed is 100mm/s~130mm/s, the polarity of the power supply is reversed
Brush Plating No. 4 Activation Solution
The solution is colorless and transparent, pH=0.2, freezing point is -18℃, and it can be stored for a long time. No. 4 activating solution has strong corrosion ability and is suitable for the activation treatment of chromium and nickel steel in passivation state or matrix materials that are still difficult to be plated after being activated by the above-mentioned activation solution. Can also be used to deburr metal and strip old coatings. The operating process specification is:
Working voltage 10V~25V
Relative movement speed 100mm/s~160mm/s Power supply polarity reversed
Brush Plating Single Metal Bath
Brush Nickel Plating Solution
1. Properties and uses of nickel
In surface plating technology, nickel is the most widely used coating. Especially used in the repair of mechanical parts and strengthening the surface of parts. This is because the nickel coating has excellent physical, chemical and mechanical properties. Nickel plating has good chemical stability in vacuum and is not easy to change color. Nickel has strong passivation ability and can quickly form a thin passivation film, so it can resist the corrosion of atmosphere, alkali and some acids well at normal temperature. For example: Nickel is very stable in organic acids, passivated in concentrated nitric acid, slowly dissolved in sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, but easily soluble in dilute nitric acid.
The brushed nickel layer has high hardness and good plasticity. Therefore, it is widely used on the surface of parts requiring high hardness and good wear resistance. Nickel also has good high temperature oxidation resistance, and the surface is oxidized only when the temperature is higher than 600 ℃.
The brush-plated nickel layer has very fine grains and has good polishing performance. The polished nickel coating can get a very bright appearance and can maintain the gloss for a long time in the atmosphere.
2. Properties, uses and process conditions of special nickel
The special nickel solution is a strong acid plating solution, pH=1, dark green in color and strong acetic acid smell. The nickel ion content in the solution is 85g/L, the density is 1.23g/cm, and the coating hardness is HB550.
The special nickel has a high bonding force with most metal substrates (except for loose materials such as cast iron), the coating is dense, and the wear resistance is good. It is mainly used to coat the bottom layer or middle sandwich layer on steel, aluminum, copper, stainless steel, chromium, nickel and other materials, and can also be used as a wear-resistant layer. When used to coat the bottom layer on stainless steel, chromium and nickel, in order to make it combine well with the substrate, it is usually directly plated with special nickel without rinsing with water after acid activation. During operation, do not energize first, use a plating pen dipped in the solution to wipe the plated surface once, after energizing, use 18V impact plating on the plated surface first, then drop to 12V, the relative movement speed is 100mm/s ~ 160mm/s, the workpiece is connected Positive power supply. 3. Performance, application and process specification of fast nickel
The solution is slightly alkaline, pH=7.5~7.8, blue-green, can smell ammonia water, nickel ion content is 53g/L, density is 1.5g/cm3, coating hardness HRC45~48. The solution is characterized by a fast deposition rate, high hardness of the coating, wear resistance, and good corrosion resistance. It can be coated with working layer, recovery layer or composite layer on various materials, more suitable for bottom coating on cast iron. The process specification is as follows:
Working voltage 10V~15V
The relative movement speed is 130mm/s~250mm/s, the polarity of the power supply is positive
Under the voltage of 10V ~ 15V and the relative movement speed of 130mm/s ~ 250mm/s, the hardness of the brush-plated rapid nickel coating is high and has good wear resistance, and its hardness and wear resistance indicators are equal to or higher than 45 The hardness and wear resistance of No. steel after quenching and tempering at 180℃. The peak of hardness appears around 12V and 180mm/s, and the size is about HV668. The peak value of wear resistance appears near 14V and 180mm/s, and the size is about 1.7 times that of No. 45 steel after quenching and tempering at 180℃.
4. Properties, uses and process specifications of basic nickel
Solution pH=8.5, blue-green color, nickel ion content 54.4g/L, coating hardness HB500. The deposition rate of the plating solution is fast and the processability is good. The coating has fine structure, uniform color, low stress and thick coating. It is suitable for plating size layer or working layer on various materials. Can be used instead of neutral nickel. The process specification is as follows:
Working voltage 8V~14V
The relative movement speed is 130mm/s~200mm/s, the polarity of the power supply is positive
5. Properties, uses and process specifications of neutral nickel
The solution was dark green, pH=7, nickel ion content was 28g/L, and the coating hardness was HB500. The deposition rate of the plating solution is fast and the processability is good. The coating structure is fine, the color is silver-white, and the corrosion resistance is good. It can be used to repair thin coatings, as the bottom layer of cast iron, and as an alternate layer of copper and acid cadmium. The process specification is as follows:
Working voltage 10V~14V
The relative movement speed is 100mm/s~160mm/s, the polarity of the power supply is positive
6. Properties, uses and process specifications of low stress nickel
This is a solution specially developed to provide a sandwich layer when depositing thick coatings. Solution pH=3.5, green color, nickel ion content 75g/L, density 1.20g/cm3, hardness HB350.
When using, the plating solution is preheated to 50°C, and a plating layer with fine structure, compressive stress or small tensile stress can be obtained. Mainly used for the sandwich layer in the composite coating, and can also be used as a protective coating. The process specification is as follows:
Working voltage 8V~14V
The relative movement speed is 100mm/s~160mm/s, the polarity of the power supply is positive
Brush copper plating solution
Copper is a rose-red metal with an atomic weight of 63.54, a density of 8.92g/cm3 and a melting point of 1083°C. Copper solution has the characteristics of fast deposition rate and moderate coating hardness, so it is widely used as a rapid recovery size layer or a thick layer. It can also be used to improve electrical conductivity, brazing, or to coat steel parts with anti-carburizing and anti-nitriding layers.
1. Properties, uses and process specifications of alkaline copper
The alkali copper solution is blue-purple, pH=9.2~9.8, the metal copper content is 62g/L, the density is 1.14g/cm3, and the coating hardness is HB250. The plating solution has fast deposition speed and low corrosiveness, and is most commonly used for rapid recovery of size layers and filling grooves; especially suitable for plating on difficult-to-plate materials such as aluminum, cast iron or zinc; It is best to prime with special nickel first, in order to obtain a higher bond. The coating structure is fine, and when the thickness is 0.01mm, it has good anti-carburization and anti-nitriding ability. Its process specification is as follows:
Working voltage 10V~14V
The relative movement speed is 100mm/s~200mm/s, the polarity of the power supply is positive
2. The properties, uses and process specifications of high-speed acid copper The solution is dark blue, pH=1.5, the metal copper content is 116g/L, the density is 1.28g/cm3, and the coating hardness is HB300. The plating solution has a high deposition rate and is mainly used for rapid recovery of size in large thicknesses and filling grooves. The plating solution is highly corrosive, and the adjacent non-plated surfaces should be well protected before plating. The coating is smooth and dense, harder than acid copper coatings, and easy to machine. When high-speed copper is plated at high current density, the grains tend to become coarse, and the continuous supply of the plating solution should be ensured. The solution cannot be directly plated on steel (except some stainless steel) and a few precious metals, and nickel should be used as a bottom layer before plating. When plating high-speed acid copper on a copper substrate, the plated surface should be wetted with this solution before electrification. Its process specification is as follows:
Working voltage 8V~14V
The relative movement speed is 160mm/s~250mm/s, the polarity of the power supply is positive
3. Properties, uses and process specifications of high-accumulation alkali copper
The plating solution is purple, pH=8.5~9.5, metal copper content is 82g/L, density is 1.28g/cm3, and coating hardness is HB250. The plating solution has a high deposition rate, can obtain a thick coating, and the coating stress is small. The plating solution is non-corrosive and has a wide range of uses, mainly for coating dimensional layers. It is especially recommended for filling pits on cadmium or tin parts and can also be used for printed circuit board repairs. Its process specification is as follows:
Working voltage 8V~14V
The relative movement speed is 130mm/s~200mm/s, the polarity of the power supply is positive
Brush Plating Alloy Bath
Alloy coating refers to a coating containing two or more metals. The alloy is divided into three structural forms: mechanical mixing, solid solution and metal compound. Alloy coating has properties that cannot be achieved by a single metal coating, and it can meet the higher requirements for the surface of metal products than a single metal coating. Alloy coatings have some excellent physical and chemical properties and mechanical properties, such as corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, high hardness and wear resistance, beautiful appearance and better brazing properties, etc. Therefore, they are widely used as protection , decorative, wear-resistant and other functional coatings. For example: nickel-tungsten, nickel-cobalt alloy coating, not only high hardness, wear resistance, but also high temperature resistance, can be used as a protective working layer for bearings, pistons, cylinders, molds and other parts.
Brush nickel-tungsten alloy solution
The solution is green, pH=2~3, the solution contains 85g/L of nickel, 15% of tungsten, and the hardness of the coating layer is HB750. The solution performance is very stable. The coating has high hardness and wear resistance. It is mainly used for the coating working layer of wear-resistant parts. The thickness of the coating is preferably within the range of 0.03mm to 0.07mm. Therefore, it can be used as a covering layer for other coatings, and a layer of acid nickel or low stress nickel can be plated first for thicker coatings. It can also be plated with special nickel alternately. During operation, each layer of nickel-tungsten alloy should be polished with oilstone or sandpaper, and then plated with special nickel after electrocleaning and No. 1 activation solution. The process specification is as follows:
Working voltage 10V~15V
The relative movement speed is 60mm/s~160mm/s, the polarity of the power supply is positive
Brush nickel-tungsten (D) alloy solution
The solution is dark green, pH=1.4~2.4, nickel content is 80g/L, and the hardness of the coating layer is HRC55. The solution has better properties than nickel-tungsten alloy, higher hardness and wear resistance; thicker plating layer can be obtained, and the residual stress is small. The hydrogen embrittlement of plating on high-strength steel is very small, and good bonding force can be obtained by plating on some difficult-to-plate metals. Mainly used for plating working layer on various parts. The process specification is the same as the nickel-tungsten alloy.
Brush Nickel-Cobalt Alloy Solution
Light green, pH=3.2, with an acidic odor at room temperature. The coating has fast deposition speed, good toughness and heat resistance, and strong coating thickness. The hardness of the coating is about HRC50 to 55. The process specifications are as follows:
Working voltage 3V~8V
The relative movement speed is 160mm/s~230mm/s, the polarity of the power supply is positive
Hot information

